
Grade
Conventional

Grade
Conventional
Facts
Molasses is a byproduct of sugar cane’s refining process. Sugar cane is mashed to create juice, and then boiled once to create cane syrup. A second boiling creates molasses.
After this syrup has been boiled a third time, a dark viscous liquid emerges known to Americans as molasses. It has the lowest sugar content of any sugar cane product.
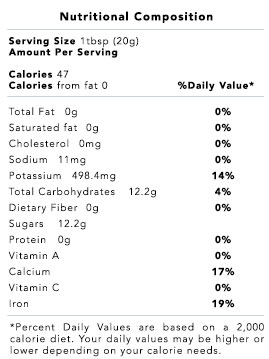
The wonderment of molasses is that it’s unlike refined sugar, which has zero nutritional value. Blackstrap molasses contains vital vitamins and minerals, such as iron, calcium, magnesium, vitamin B6, and selenium.
Preliminary Health Research
1. Diabetes-Friendly Sweetener
If you have diabetes and a sweet tooth, you have a bit of a conundrum. While molasses is derived from sugar and adds as many carbohydrates as other sugars, it may be digested more slowly, which may help stabilize blood sugar.
2. Bone Booster
Everyone knows that calcium is needed for strong bones, but not everyone knows the importance that magnesium plays in growing them.
Molasses contains both calcium and magnesium, so it can help you guard against osteoporosis. About 5 tablespoons of molasses contains 50 percent of the recommended daily allowance of calcium, 95 percent of iron, and 38 percent of magnesium.
Low levels of magnesium are also crucial in preventing diseases like osteoporosis and asthma along with others that can affect your blood and heart.
3. Good for the Blood
People with anemia — a condition in which your body doesn’t have enough red blood cells — often feel tired and weak. One type of anemia is caused by a lack of iron in the diet.
Molasses is a good source of iron. About 5 tablespoons of molasses contains 95 percent of your daily allowance of iron.
4. Packed with Potassium
Bananas may be king when it comes to potassium, but molasses is also packed with the stuff.
Uses
You can use blackstrap molasses in baking sweet treats. It’s what gives gingerbread cookies their distinctive rich flavor.
Besides adding it into recipes, you can add it to hot water and drink warm or cold as a dietary supplement.
Try mixing molasses in with baked beans, or even use it as a basting glaze on chicken, turkey, or other meats. A spoonful straight eaten directly can also give you a quick boost.